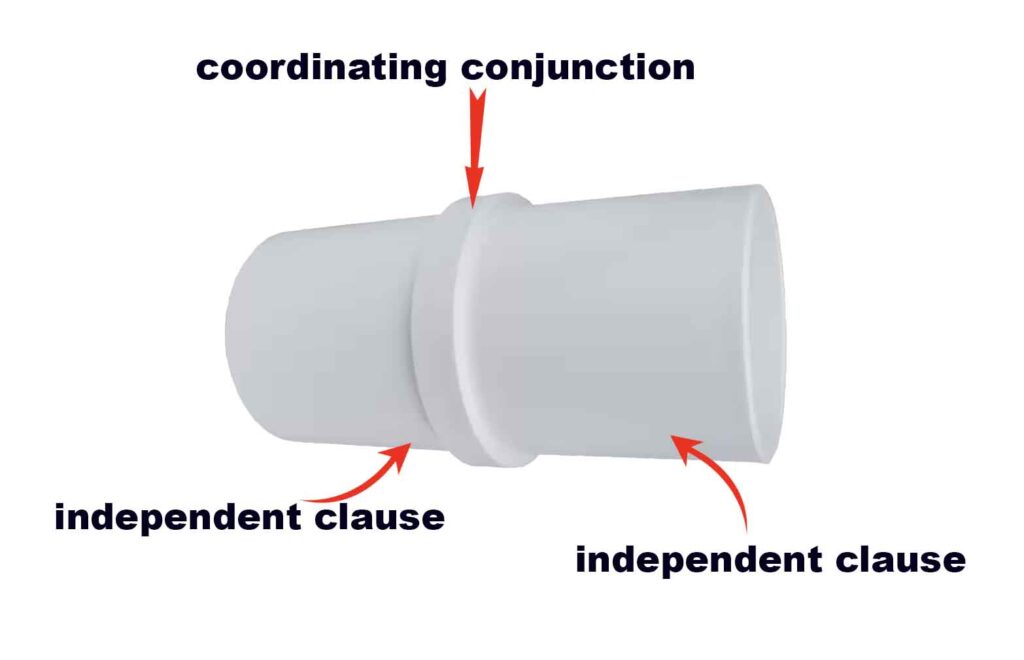
Subordinating conjunctions link two parts of a sentence, making it more complex. They connect a dependent clause (incomplete thought) to an independent clause (complete thought). These words, like after, because, and when, show relationships like time, cause-and-effect, or contrast between the clauses.
Examples:
- After: ശേഷം
It is used to indicate that one event will occur following another event.
Example: After I finish my work, I will go for a walk.
I will go for a walk after I finish my work. (no comma)
- Although/ Though/ Eventhough: എങ്കിലും, ആയിരുന്നാലും, എന്നിട്ടും, ആണെങ്കിലും
It is used to express a contrast or contradiction.
Example: Although it was raining, we decided to go for a picnic.
We decided to go for a picnic, although it was raining. (need comma in both formation)
- As: ആ സമയത്ത് , ആയതിനാൽ
It is used to indicate that two actions are happening simultaneously.
Example: As I was walking to the store, I saw a friend.
As I was not well, I din’t go to school.
I didn’t go to school as I was sick (no need for comma)
- Because: അതുകൊണ്ട്
It is used to indicate the reason for something.
Example: I couldn’t attend the party because I was feeling sick.
Because I was feeling sick, I couldn’t attend the party. (need comma)
- Before: മുമ്പ്
It used to indicate that one event will occur prior to another event.
Example: Before you judge others, (you) judge yourself. (need comma)
Judge yourself before you judge others (no need of comma)
- Even if: എന്നാലും
It is used to express a hypothetical or unlikely situation.
Example: Even if it rains tomorrow, we will still go to the beach.
We will still go to the beach even if it rains tomorrow.
- If: എങ്കിൽ
It is used to express a hypothetical or conditional situation.
Example: If I study hard, I can pass the exam. (need comma)
I can pass the exam if I study hard. (no need of comma)
- In order that: അതിനായി
It is used to express purpose or intent.
Example: I will study hard in order that I can get a good grade on the test.
In order that I can get a good grade on the test, I will study hard.
- In order to: ഇതിനായി
In order to get good sleep, one should go to bed early.
One should go to bed early in order to get good sleep.
- Once: ഒരു കാര്യം പൂർത്തിയാക്കിയ ശേഷം
It is used to indicate that an event will occur after another event has taken place.
Example: Once you reach home, please call me.
Please call me once you reach home.
- Provided that ഒരു വ്യവസ്ഥ നിറവേറ്റിയാൽ
It is used to express a condition that must be met in order for something to happen
Example:I will give you a promotion provided that you achieve your target.
Provided that you achieve your target, I will give you a promotion.
- Since ആയതിനാൽ, അതുകൊണ്ട്
Example: Since it’s raining outside, we decided to have a cozy movie night indoors.
- So that: അതുകൊണ്ട്
It is used to express purpose or intent.
Example: I will study hard so that I can get a good grade on the test.
So that I can get a good grade on the test, I will study hard.
- Unless അല്ലാതെ
it is used to express a condition that must be met in order for something to happen.
Example: I won’t be able to attend the meeting unless I finish my work on time.
- Until അതുവരെ
It is used to indicate that an event will continue until another event occurs. (time)
Example: I will keep working until I finish the project.
- When ആ സമയത്ത്
It is used to indicate that an event will occur at the same time as another event.
Example: When you reach, please call me.
Please call me when you reach.
- Whereas: അതേസമയം
It is used to express a contrast or comparison
Example: She likes action movies, whereas I prefer romantic comedies.
- Wherever: എവിടെയായിരുന്നാലും
It is used to indicate any place where something may happen.
Example: I will follow you wherever you go.
Wherever you go, I will follow you.
- While: അതെ സമയം
It is a conjunction that is commonly used to indicate a contrast, opposition, or simultaneous occurrence of two actions. Its meaning can vary depending on the context in which it’s used. Here are a few common uses of “while” as a conjunction:
A. Contrast:
She enjoys reading while her brother prefers playing video games.
While some people prefer summer, others prefer winter.
B. Simultaneous Action:
I listened to music while I worked on my assignment.
He ate dinner while watching TV.
C. Time:
I met her while I was studying abroad.
While I was in the store, I ran into an old friend.
More examples of subordinating conjunctions
1. After:
– After the rain stopped, we went outside to play.
– We went outside to play after the rain stopped.
– After I finish my chores, I’ll join you for dinner.
– I’ll join you for dinner after I finish my chores.
2. Although:
– Although it was late, she decided to go for a run.
– She decided to go for a run, although it was late.
– Although he studied hard, he still failed the exam.
– He still failed the exam, although he studied hard.
3. As:
– As I was walking to the store, I saw an old friend.
– I saw an old friend as I was walking to the store.
– She smiled at me as if she knew something I didn’t.
– As if she knew something I didn’t, she smiled at me.
4. As if:
– He acted as if he had never seen a dog before.
– He had never seen a dog before, as if he acted.
– She looked at me as if I had grown another head.
– As if I had grown another head, she looked at me.
5. As long as:
– You can stay up late as long as you finish your homework.
– As long as you finish your homework, you can stay up late.
– As long as the food is delicious, I’ll eat anything.
– I’ll eat anything as long as the food is delicious.
6. As much as:
– As much as I love ice cream, I know it’s not good for me.
– I know it’s not good for me, as much as I love ice cream.
– As much as he wanted to go on vacation, he couldn’t afford it.
– He couldn’t afford it, as much as he wanted to go on vacation.
7. As soon as:
– As soon as the bell rings, you can leave the classroom.
– You can leave the classroom as soon as the bell rings.
– She knew the answer as soon as the question was asked.
– As soon as the question was asked, she knew the answer.
8. As though:
– He acted as though he had seen a ghost.
– He had seen a ghost, as though he acted.
– She talked to me as though I were a child.
– As though I were a child, she talked to me.
9. Because:
– They cancelled the picnic because of the bad weather.
– Because of the bad weather, they cancelled the picnic.
– She didn’t go to the party because she wasn’t feeling well.
– Because she wasn’t feeling well, she didn’t go to the party.
10. Before:
– Before she goes to bed, she reads a book.
– She reads a book before she goes to bed.
– He likes to have his coffee before he starts work.
– Before he starts work, he likes to have his coffee.
11. By the time:
– By the time she arrived, the party was already over.
– The party was already over by the time she arrived.
– By the time we finish the project, the deadline will have passed.
– The deadline will have passed by the time we finish the project.
12. Even if:
– Even if it rains, we’ll still go to the beach.
– We’ll still go to the beach, even if it rains.
– Even if he apologizes, I’m not sure I can forgive him.
– I’m not sure I can forgive him, even if he apologizes.
13. Even though:
– Even though it was his birthday, he didn’t want to celebrate.
– He didn’t want to celebrate, even though it was his birthday.
– Even though she studied hard, she failed the exam.
– She failed the exam, even though she studied hard.
14. If:
– If it rains, we’ll stay indoors.
– We’ll stay indoors if it rains.
– If he arrives late, we’ll start without him.
– We’ll start without him if he arrives late.
15. Inasmuch as:
– Inasmuch as I appreciate the offer, I have to decline.
– I have to decline inasmuch as I appreciate the offer.
– Inasmuch as he wants to help, he doesn’t know how.
– He doesn’t know how, inasmuch as he wants to help.
16. In case:
– Take an umbrella in case it rains.
– In case it rains, take an umbrella.
– I brought some snacks in case we get hungry.
– In case we get hungry, I brought some snacks.
17. In order that:
– I’ll leave early in order that I can catch the train.
– In order that I can catch the train, I’ll leave early.
– She turned up the volume in order that she could hear better.
– In order that she could hear better, she turned up the volume.
18. Lest:
– Turn off the lights lest they attract mosquitoes.
– Lest they attract mosquitoes, turn off the lights.
– She wrote a reminder lest she forget about the meeting.
– Lest she forget about the meeting, she wrote a reminder.
19. Now that:
– Now that we’re here, let’s enjoy ourselves.
– Let’s enjoy ourselves, now that we’re here.
– Now that he has a job, he can afford to buy a car.
– He can afford to buy a car, now that he has a job.
20. Once:
– Once you finish your homework, you can go out and play.
– You can go out and play once you finish your homework.
– Once the sun sets, it will be too dark to play outside.
– It will be too dark to play outside once the sun sets.
21. Provided (that):
– You can go to the party provided that you finish your homework first.
– Provided that you finish your homework first, you can go to the party.
– We can go for a walk provided that it stops raining.
– Provided that it stops raining, we can go for a walk.
22. Rather than:
– He chose to walk rather than take the bus.
– Rather than take the bus, he chose to walk.
– She decided to apologize rather than argue further.
– Rather than argue further, she decided to apologize.
23. Since:
– Since it’s already late, let’s go to bed.
– Let’s go to bed since it’s already late.
– Since he already knows the answer, there’s no need to ask him.
– There’s no need to ask him since he already knows the answer.
24. So that:
– He opened the window so that fresh air could come in.
– So that fresh air could come in, he opened the window.
– She left a note on the table so that we wouldn’t forget.
– So that we wouldn’t forget, she left a note on the table.
25. Supposing (that):
– Supposing that you don’t pass the test, what will you do?
– What will you do, supposing that you don’t pass the test?
– Supposing that it rains, we should bring umbrellas.
– We should bring umbrellas, supposing that it rains.
26. Than:
– She is taller than her sister.
– Her sister is shorter than she is.
– He would rather walk than take the bus.
– Than take the bus, he would rather walk.
27. That:
– He said that he would come to the party.
– I know that you can do better than this.
– She believes that honesty is the best policy.
– It’s possible that she forgot about the meeting.
28. Though:
– Though it was raining, they decided to go for a walk.
– They decided to go for a walk, though it was raining.
– He failed the exam, though he studied hard.
– Though he studied hard, he failed the exam.
29. Till:
– We’ll wait here till you arrive.
– Till you arrive, we’ll wait here.
– He worked till late in the night to finish the project.
– Till late in the night, he worked to finish the project.
30. Unless:
– Unless you apologize, I won’t forgive you.
– I won’t forgive you unless you apologize.
– We won’t be able to go out unless the rain stops.
– Unless the rain stops, we won’t be able to go out.
31. Until:
– We’ll wait here until you finish your presentation.
– Until you finish your presentation, we’ll wait here.
– She stayed up until midnight studying for her exam.
– Until midnight, she stayed up studying for her exam.
32. When:
– I’ll call you when I reach the airport.
– When I reach the airport, I’ll call you.
– He always gets nervous when he has to speak in public.
– When he has to speak in public, he always gets nervous.
33. Whenever:
– Whenever she hears that song, it reminds her of her childhood.
– It reminds her of her childhood whenever she hears that song.
– He always brings flowers whenever he visits his grandmother.
– Whenever he visits his grandmother, he always brings flowers.
34. Where:
– This is where we first met.
– We first met where you’re standing.
– She looked everywhere to find her keys, but she couldn’t remember where she left them.
– She couldn’t remember where she left them, even though she looked everywhere to find her keys.
35. Whereas:
– She enjoys sweet foods, whereas her sister prefers savory dishes.
– Whereas her sister prefers savory dishes, she enjoys sweet foods.
– He enjoys spending time outdoors, whereas his brother prefers staying indoors.
– Whereas his brother prefers staying indoors, he enjoys spending time outdoors.
36. Wherever:
– She’ll follow her dreams wherever they may lead.
– Wherever they may lead, she’ll follow her dreams.
– He always carries his camera wherever he goes.
– Wherever he goes, he always carries his camera.
37. Whether:
– Whether you like it or not, we have to finish this project by tomorrow.
– We have to finish this project by tomorrow, whether you like it or not.
– She couldn’t decide whether to go to the party or stay home.
– Whether to go to the party or stay home, she couldn’t decide.
38. While:
– I like to listen to music while I’m working.
– While I’m working, I like to listen to music.
– She called her friend while she was waiting for the bus.
– While she was waiting for the bus, she called her friend.
39. Because of:
– She couldn’t attend the meeting because of a family emergency.
– Because of a family emergency, she couldn’t attend the meeting.
– He was late to the party because of heavy traffic.
– Because of heavy traffic, he was late to the party.
40. In spite of:
– In spite of the rain, they decided to go for a picnic.
– They decided to go for a picnic in spite of the rain.
– In spite of his busy schedule, he always finds time for his hobbies.
– He always finds time for his hobbies in spite of his busy schedule.
41. Despite:
– Despite the bad weather, they went ahead with the outdoor party.
– They went ahead with the outdoor party despite the bad weather.
– Despite his busy schedule, he always finds time for his family.
– He always finds time for his family despite his busy schedule.
42. Even when:
– Even when it’s late, he insists on finishing his work.
– He insists on finishing his work even when it’s late.
– Even when she was tired, she kept practicing the piano.
– She kept practicing the piano even when she was tired.
43. Whether or not:
– Whether or not she agrees, we’re going ahead with the plan.
– We’re going ahead with the plan whether or not she agrees.
– Whether or not it rains, the picnic will still take place.
– The picnic will still take place whether or not it rains.
44. No matter:
– No matter what happens, I’ll always be there for you.
– I’ll always be there for you, no matter what happens.
– No matter how hard she tries, she can’t seem to please everyone.
– She can’t seem to please everyone, no matter how hard she tries.
45. So long as:
– You can use my car so long as you fill up the tank afterward.
– So long as you fill up the tank afterward, you can use my car.
– He’s allowed to play video games so long as he finishes his homework first.
– So long as he finishes his homework first, he’s allowed to play video games.
46. In the event that:
– In the event that the power goes out, we have flashlights and candles.
– We have flashlights and candles in the event that the power goes out.
– He packed an extra jacket in the event that it gets cold.
– In the event that it gets cold, he packed an extra jacket.
47. Insofar as:
– Insofar as I know, the meeting is still scheduled for tomorrow.
– The meeting is still scheduled for tomorrow, insofar as I know.
– She followed the instructions insofar as she understood them.
– Insofar as she understood them, she followed the instructions.
48. Provided (that):
– You can borrow my car provided that you return it by Friday.
– Provided that you return it by Friday, you can borrow my car.
– We’ll go to the beach provided that the weather stays nice.
– Provided that the weather stays nice, we’ll go to the beach.
49. Whether or not:
– Whether or not he apologizes, I won’t forgive him.
– I won’t forgive him whether or not he apologizes.
– Whether or not they win the game, they’ll still celebrate.
– They’ll still celebrate whether or not they win the game.
50. Seeing that:
– Seeing that you’re tired, let’s call it a day and continue tomorrow.
– Let’s call it a day and continue tomorrow, seeing that you’re tired.
– Seeing that she’s upset, he decided to postpone the conversation.
– He decided to postpone the conversation, seeing that she’s upset.