Text A Hypertension is one of the most common lifestyle diseases to date. It affects people from all walks of life. Let us get to know hypertension more by its definitions.
Hypertension is defined as a systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of more than 90 mmHg. This is based on the average of two or more accurate blood pressure measurements during two or more consultations with the healthcare provider. The definition is taken from the Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure.
Text B Etiology and pathophysiology
1. Etiology is complex; begins insidiously; changes in arteriolar bed cause increased resistance; increased blood volume may result from hormonal or renal dysfunction; arteriolar thickening causes increased peripheral vascular resistance; abnormal renin release constricts arterioles
a. 90% to 95% have an unidentifiable cause (essential or primary hypertension);multiple factors such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism, sympathetic nervous system activity, and insulin resistance may be involved
b. 5% to 10% have identifiable causes (secondary hypertension); pathophysiology is related to condition causing the rise in pressure; conditions include Reno vascular disease; primary hyperaldosteronism; Cushing’s syndrome; diabetes mellitus; neurologic disorders; dysfunction of thyroid, pituitary, or parathyroid glands; coarctation of the aorta; and pregnancy Classification of BP by the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7) (JNC 8 will be available summer 2011)
a. Normal: systolic less than 120 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg
b. Prehypertension: systolic 120 to 139 mm Hg or diastolic 80 to 89 mm Hg
c. Stage 1 hypertension: systolic 140 to 159 mm Hg or diastolic 90 to 99 mm Hg d. Stage 2 hypertension: systolic 160 mm Hg or more, or diastolic 100 mm Hg or more
TEXT C
Text D Care of Clients with Hypertension Assessment/Analysis
1. Vital signs in both upright and recumbent positions; use appropriate cuff (width should be 40% of the arm’s circumference); avoid errors of parallax when readings phygmomanometer
2. Baseline weight
3. Presence of risk factors and clinical evidence of target organ damage
Planning/Implementation
1. Monitor levels of electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, lipid profile, and urine for protein
2. Encourage weight reduction if indicated; weigh daily to monitor fluid balance when there is threat of heart failure
3. Teach to monitor own BP; a BP of 180/120 mm Hg or higher represents a hypertensive emergency; advise to change position slowly and avoid hot showers to prevent orthostatic hypotension when taking antihypertensives
4. Support expression of emotions; encourage relaxation techniques
5. Reinforce that hypertension is not cured, but controlled
PART A TIME: 15 minutes.
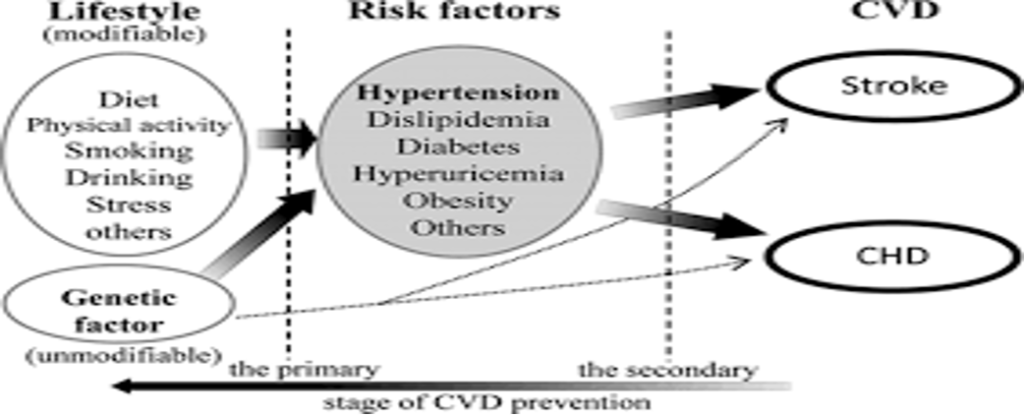
1. Stages of CVD prevention …………….
2. Assessment of baseline weight ………………..
3. Hypertension affects people from all walks life ………….
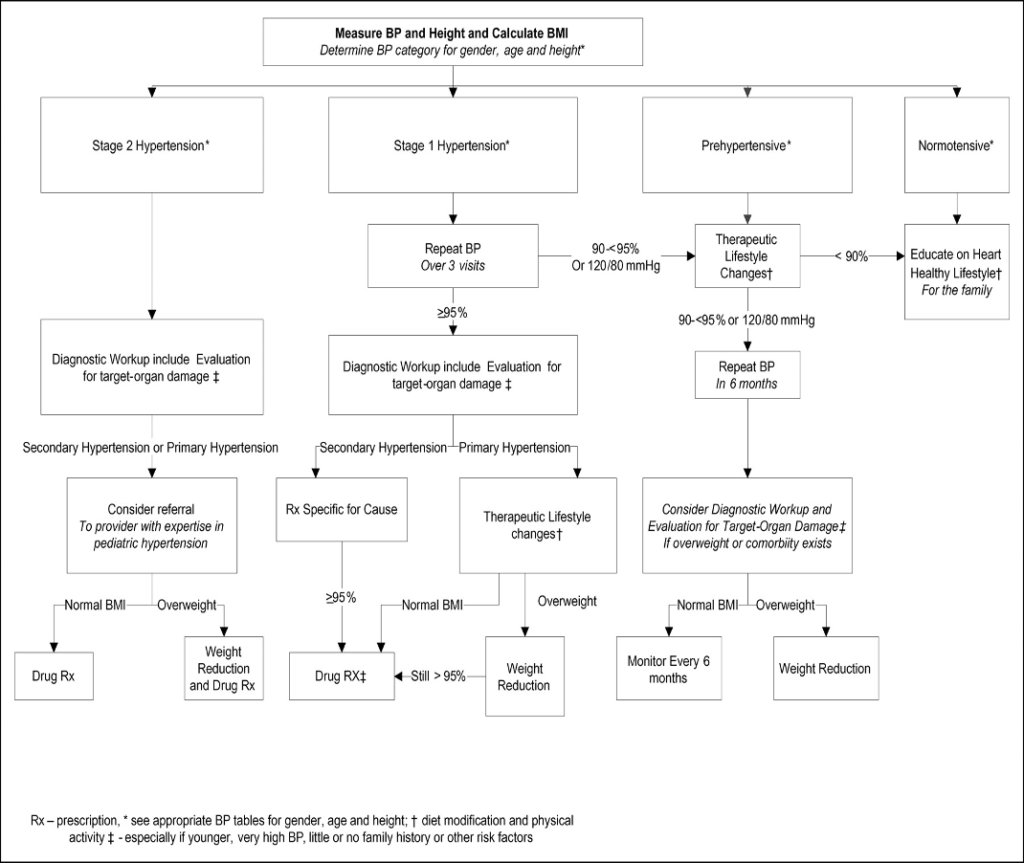
4. The range of blood pressure represents stage I hypertension ………….
5. Checking vital signs in both upright and recumbent positions ………….
6. Causes of hypertension ……………
7. Teaching client to check his/her own BP ……………
Questions 8-14. Answer each of the questions, 8-4, with a word or short phrase from one of the texts. Each answer may include words, number of the both. Your answers should be correctly spelled.
8. What is the minimum diastolic pressure in person with pre hypertension?
9. The client who is with normal blood pressure should be educated on what?
10. What should be avoided while reading sphygmomanometer?
11. What must be checked daily to monitor fluid balance when there is threat of heart failure?
12. What is the maximum systolic pressure in client with stage 1 hypertension?
13. The client with over weight is required to be encouraged on …………?
14. In how many visits the BP should be checked once the stage 1 hypertension is determined?
Questions 15-20. Complete each of the sentences, 15- 20, with a word or short phrase from one of the texts. Each answer may include words, number or both. Your answers should be correctly spelled
15. Presence of risk factors and …………. of target organ damage are assessed in the hypertensive patients.
16. Hypertension is one of the most common ………………..diseases to date.
17. The definition of hypertension is taken from the ………………. report of the joint National Committee
18. ………………..% have identifiable causes (secondary hypertension )
19. Reinforce that hypertension is not……. but controlled.
20. Monitor levels of electrolytes, BUN…….. lipid profile and urine for protein.
Free admission and English Courses. കാശ് കൊടുക്കാതെ അഡ്മിഷൻ. FREE ഇഗ്ലീഷ് കോഴ്സുകൾ. ഈ ഓഫർ നേടൂ. Contact us at +91 9886926773 പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് ആയാസകരം.

New batch is open. Join today!

Ready to study abroad or master OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English?
📞 Call us now at +91 9886926773
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: mail@goltc.in
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
Would you like to download a copy of the practice test? Please click on the download button below:


Pingback: HYPERTENSION OET READING | Lifestyle Training Centre®
Pingback: HYPERTENSION OET READING ANSWERS | Lifestyle Training Centre®