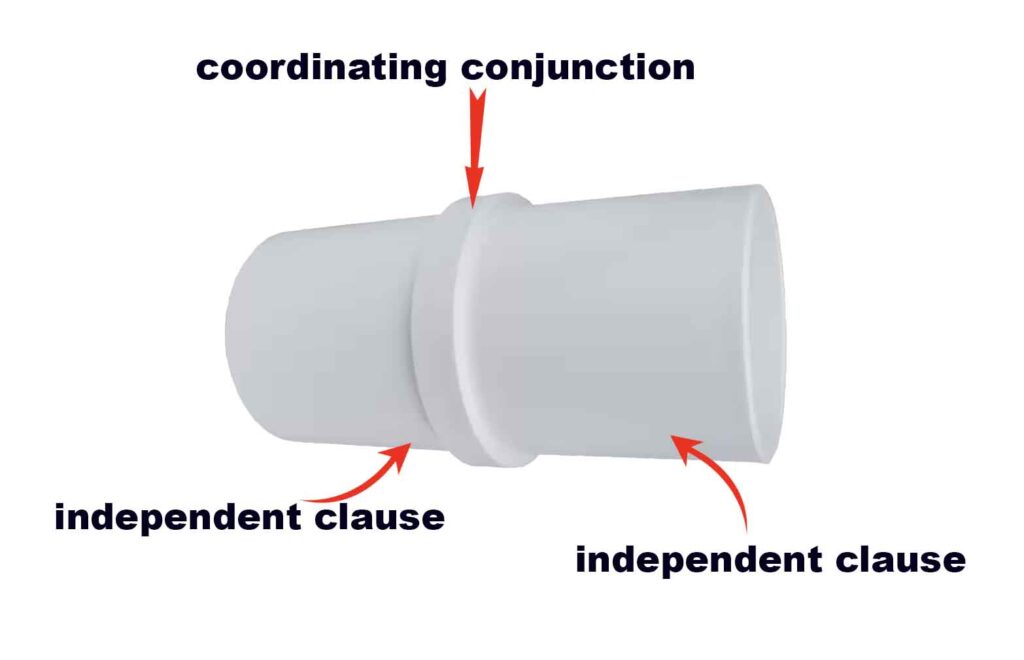
Do not start a sentence with coordinating conjunctions. Use them in between
Conjunctions and Their Malayalam Meanings
| Conjunctions | |
|---|---|
| Coordinating Conjunctions (FANBOYS) | |
| For | കാരണമായ് |
| Meaning: Used to explain reasons. ഒരു ഉദ്ദേശം, കാരണം, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ലക്ഷ്യം സൂചിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. വേണ്ടി, കാരണം, നിമിത്തം, ഉദ്ദേശിച്ച്, ലക്ഷ്യത്തിൽ, പ്രയോജനത്തിന്, ആഗ്രഹിച്ച്, ആവശ്യമായി. Examples: 1. He stayed home, for he was sick. 2. She left early, for she had an appointment. 3. I took an umbrella, for it looked like rain. | |
| And | കൂടാതെ |
| Meaning: Used to connect similar ideas. രണ്ടോ അതിലധികമോ വസ്തുക്കളെ, ആശയങ്ങളെ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വാക്യഭാഗങ്ങളെ ബന്ധിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഒരു ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. കൂടാതെ, അതോടൊപ്പം, പിന്നെയും, മേലധികം, ഇനിയുമധികം, ഒപ്പം, കൂടിയോ. Examples: 1. She bought apples, and he bought oranges. 2. We went to the park, and they went shopping. 3. He came home and went to sleep. | |
| Nor | അതുമില്ല |
| Meaning: Used to show a negative addition. ഒന്നും അല്ല, അതും അല്ല എന്നതുപോലെ രണ്ടും അല്ലെന്ന് സൂചിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഒരു ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. അതുമില്ല, ഇതുമില്ല, ഒരുമല്ല, ഇല്ലാത്തതുപോലെ, ഒന്നുമല്ല. Examples: 1. She doesn’t like coffee, nor does she like tea. 2. He didn’t call, nor did he send a message. 3. He didn’t study nor pass the test. | |
| But | പക്ഷേ |
| Meaning: Used to show contrast. മുൻപുള്ള പ്രസ്താവനയ്ക്കു വിരുദ്ധമായ ഒരു ആശയം അവതരിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. പക്ഷേ, എന്നാൽ, എന്നിരുന്നാലും, അതേസമയം, എന്നാലും. Examples: 1. He is tall, but she is short. 2. I wanted to go out, but it was raining. 3. She tried her best but couldn’t win. | |
| Or | അല്ലെങ്കിൽ |
| Meaning: Used to present alternatives. രണ്ട് അല്ലെങ്കിൽ അതിൽ കൂടുതൽ സാധ്യതകൾ നിരീക്ഷിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. അല്ലെങ്കിൽ, അതോ, അതല്ലെങ്കിൽ, വേണ്ടെങ്കിൽ. Examples: 1. Do you want tea, or do you want coffee? 2. We can go now, or we can wait for them. 3. You can take a bus or walk. | |
| Yet | എന്നിരുന്നാലും, എന്നിട്ടും |
| Meaning: Shows contrast despite previous information. പ്രതീക്ഷിച്ചതിനൊപ്പമുള്ള വൈരുദ്ധ്യമായ പരിസ്ഥിതി സൂചിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. എന്നിരുന്നാലും, ഇതുവരെ, എങ്കിലും, പക്ഷേ. Examples: 1. It was raining, yet they went out. 2. She was tired, yet she kept working. 3. She felt sick yet continued working. | |
| So | അതിനാൽ |
| Meaning: Shows result or consequence. ഒരു കാരണത്തിൻറെ ഫലമായി വരുന്ന അനിവാര്യമായ മാറ്റം സൂചിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ബന്ധകസംയോഗം. അതിനാൽ, അതിനുകൊണ്ട്, അതിനാൽപ്പറ്റി. Examples: 1. He was tired, so he went to bed early. 2. It was late, so they left quickly. 3. He studied hard so passed the exam. | |
Coordinating Conjunctions (FANBOYS)
Full Guide with Malayalam & English Examples + Exercises
What is a Coordinating Conjunction?
A coordinating conjunction is a word used to connect two or more words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance in a sentence. These conjunctions help in forming compound sentences, joining coordinate adjectives, and linking phrases or words effectively.
🔹 Mnemonic to remember them: FANBOYS
- F – For (കാരണം)
- A – And (മാത്രമല്ല)
- N – Nor (അതും ഇല്ല)
- B – But (പക്ഷെ)
- O – Or (അല്ലെങ്കിൽ)
- Y – Yet (എന്നിട്ടും)
- S – So (അതുകൊണ്ട്)
Detailed Explanation & Examples
1. FOR (കാരണം) – Shows Reason or Explanation
📝 Usage: Used to explain why something happens. Similar to “because.”
✅ Examples:
- He scored good marks, for he had studied well.
(അവൻ നല്ല മാർക്ക് നേടി, കാരണം അവൻ നല്ലപോലെ പഠിച്ചിരുന്നു.) - She was worried, for her friend was not answering the phone.
(അവൾ വിഷമിച്ചു, കാരണം അവളുടെ സുഹൃത്ത് ഫോണിൽ പ്രതികരിച്ചില്ല.)
2. AND (മാത്രമല്ല) – Adds Information
📝 Usage: Used to add information to a sentence.
✅ Examples:
- He came early, and he slept off.
(അവൻ നേരത്തേ എത്തി, അതിനുശേഷം ഉറങ്ങി.) - She bought a dress and a handbag.
(അവൾ ഒരു ഫ്രോക്ക് മറ്റും ഒരു ഹാൻഡ്ബാഗും വാങ്ങി.)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- He came early and slept off.
- She cooked dinner and cleaned the kitchen.
3. NOR (അതും ഇല്ല) – Adds a Negative Idea
📝 Usage: Used to connect two negative statements. Often follows “neither.”
✅ Examples:
- He did not come to the party, nor did he call to inform.
(അവൻ പാർട്ടിക്ക് വന്നില്ല, അതുപോലെ അറിയിക്കാനും വിളിച്ചില്ല.) - She doesn’t like coffee, nor does she like tea.
(അവൾക്ക് കോഫി ഇഷ്ടമല്ല, അതുപോലെ തന്നെ ചായയുമില്ല.)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- He didn’t call nor message me.
- She doesn’t watch movies nor listen to music.
4. BUT (പക്ഷെ) – Shows Contrast
📝 Usage: Used to show contrast between two ideas.
✅ Examples:
- I drink tea, but I do not use sugar.
(ഞാൻ ചായ കുടിക്കും, പക്ഷേ പഞ്ചസാര ചേർക്കില്ല.) - She is intelligent, but lazy.
(അവൾ ബുദ്ധിയുള്ളവളാണ്, പക്ഷേ സോമ്മിയായിരിക്കുന്നു.)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- He tried his best but couldn’t win.
- She loves painting but doesn’t have time for it.
5. OR (അല്ലെങ്കിൽ) – Presents Alternatives
📝 Usage: Used to offer a choice between two possibilities.
✅ Examples:
- You can try IELTS, or you can try OET.
(നിങ്ങൾ IELTS ശ്രമിക്കാം, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ OET ശ്രമിക്കാം.) - Would you like tea, or coffee?
(നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ചായ വേണോ, അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കോഫിയോ?)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- You can try IELTS or OET.
- We can go to the park or stay home.
6. YET (എന്നിട്ടും) – Shows Unexpected Contrast
📝 Usage: Used to show contrast when something unexpected happens.
✅ Examples:
- He came early, yet he didn’t get the bus.
(അവൻ നേരത്തേ എത്തി, എന്നിട്ടും ബസ് കിട്ടിയില്ല.) - She was tired, yet she kept working.
(അവൾ ക്ഷീണിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു, എന്നിട്ടും ജോലി തുടർന്നു.)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- He studied well yet failed the exam.
- She was scared yet jumped off the cliff.
7. SO (അതുകൊണ്ട്) – Shows Cause & Effect
📝 Usage: Used to show a result or consequence.
✅ Examples:
- He studied well, so he passed the exam.
(അവൻ നല്ലപോലെ പഠിച്ചു, അതുകൊണ്ടു അവൻ പരീക്ഷ പാസായി.) - It was raining, so we stayed inside.
(മഴപെയ്തു, അതിനാൽ ഞങ്ങൾ അകത്തായിരുന്നു.)
📝 Shared Subject Sentences:
- He was hungry so ate quickly.
- She missed the bus so walked home.
📝 Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Choose the correct coordinating conjunction:
- I like both ice cream ____ chocolate. (and/or)
- He was sick, ____ he went to the doctor. (so/but)
- She can sing ____ dance very well. (and/nor)
- He was tired, ____ he continued working. (yet/so)
- Do you want coffee ____ tea? (or/and)
- He didn’t eat breakfast, ____ did he drink water. (nor/so)
📝 Exercise 2: Rewrite with Shared Subjects
Rewrite these sentences by sharing the subject:
- He went to the market. He bought vegetables.
→ He went to the market and bought vegetables. - She was tired. She didn’t sleep.
→ She was tired but didn’t sleep. - They practiced a lot. They won the match.
→ They practiced a lot so won the match. - I can read. I can write.
→ I can read and write.
Practice set for mastering Coordinating Conjunctions (FANBOYS) with answer keys
📝 Set 1-10: Fill in the Blanks
Options: (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so)
- He was late, ____ he missed the train.
- She studied hard, ____ she passed the exam.
- I like coffee, ____ I don’t like tea.
- We can go by car, ____ we can take a train.
- He didn’t call, ____ did he send a message.
- She tried her best, ____ she still failed.
- He eats a lot, ____ he never gains weight.
- Do you want pizza ____ a burger?
- It was raining, ____ we stayed inside.
- She is very rich, ____ she lives a simple life.
✅ Answer Key
- so
- so
- but
- or
- nor
- yet
- yet
- or
- so
- yet
📝 Set 11-20: Sentence Rewriting (Shared Subject)
Rewrite each sentence by sharing the subject.
- She woke up early. She went for a walk.
- He was tired. He didn’t stop working.
- We can watch a movie. We can go for dinner.
- I tried calling him. He didn’t answer.
- They were angry. They did not shout.
- You can stay here. You can leave.
- He didn’t like apples. He didn’t like bananas.
- The dog barked. The cat ran away.
- She worked hard. She got promoted.
- He left the office. He went home.
✅ Answer Key
- She woke up early and went for a walk.
- He was tired but didn’t stop working.
- We can watch a movie or go for dinner.
- I tried calling him but he didn’t answer.
- They were angry yet did not shout.
- You can stay here or leave.
- He didn’t like apples nor bananas.
- The dog barked so the cat ran away.
- She worked hard so got promoted.
- He left the office and went home.
📝 Set 21-30: Multiple Choice Questions
Select the correct coordinating conjunction.
- I wanted to go for a walk, ____ it was raining heavily.
a) and
b) but
c) so - He was feeling unwell, ____ he still went to work.
a) yet
b) or
c) nor - Would you like tea ____ coffee?
a) and
b) or
c) for
- She was sad, ____ she smiled anyway.
a) but
b) so
c) for - He did not study, ____ did he practice.
a) and
b) nor
c) but - I was tired, ____ I took a nap.
a) yet
b) so
c) for - He is funny, ____ he is kind.
a) but
b) and
c) so - You should sleep early, ____ you have an exam tomorrow.
a) for
b) yet
c) so - They called me, ____ I didn’t answer.
a) or
b) yet
c) for - She likes chocolates, ____ she does not eat them often.
a) but
b) so
c) nor
✅ Answer Key
- b) but
- a) yet
- b) or
- a) but
- b) nor
- b) so
- b) and
- c) so
- b) yet
- a) but
📝 Set 31-40: Fill in the Blanks (Advanced)
Options: (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so)
- She speaks French, ____ she doesn’t understand Spanish.
- I missed the bus, ____ I took a taxi.
- He enjoys reading, ____ he dislikes writing.
- The movie was long, ____ it was very interesting.
- They wanted to leave early, ____ they stayed for the party.
- You can have pasta, ____ you can order pizza.
- He was nervous, ____ he delivered a great speech.
- I forgot to set an alarm, ____ I woke up late.
- We should hurry, ____ we will miss the flight.
- The weather was hot, ____ the kids played outside.
✅ Answer Key
- but
- so
- but
- yet
- yet
- or
- yet
- so
- or
- yet
📝 Set 41-50: Sentence Correction
Find and correct the incorrect conjunction.
- He loves singing, so he doesn’t enjoy dancing. (Incorrect: so)
- She is rich, nor she lives a luxurious life. (Incorrect: nor)
- The road was slippery, and the driver lost control. (Incorrect: and)
- You should study more, for you will fail. (Incorrect: for)
- She wanted ice cream, but she ordered a salad. (Incorrect: but)
- He trained hard, yet won the match. (Incorrect: yet)
- The baby was crying, and the mother tried to comfort him. (Incorrect: and)
- He neither ate breakfast, nor he drank coffee. (Incorrect: nor he drank)
- I wanted to buy a car, but I didn’t have enough money. (Correct or Incorrect?)
- We can go to the beach, for we can visit the mountains. (Incorrect: for)
✅ Answer Key
- but
- yet
- so
- or
- yet
- so
- so
- nor did he drink
- Correct
- or
FAQ
1. What are coordinating conjunctions?
Coordinating conjunctions are words that connect two or more words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal grammatical rank in a sentence. The most common coordinating conjunctions are FANBOYS: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So.
2. What is the function of coordinating conjunctions?
Coordinating conjunctions are used to:
- Link two independent clauses (compound sentences).
- Connect words or phrases of the same grammatical type.
- Show relationships like addition, contrast, choice, cause-effect, etc.
3. What is the FANBOYS rule?
FANBOYS is an acronym for the seven coordinating conjunctions:
- F – For (reason/cause)
- A – And (addition)
- N – Nor (negative alternative)
- B – But (contrast)
- O – Or (choice/alternative)
- Y – Yet (unexpected contrast)
- S – So (result/consequence)
4. Can coordinating conjunctions start a sentence?
Yes, but it’s often informal. Example:
- But I didn’t have time to finish the task.
- And she decided to leave early.
They are originally used in between two independent clauses.
5. What is the difference between coordinating and subordinating conjunctions?
Coordinating conjunctions connect two independent clauses or equal elements. Example: He studied hard, so he passed.Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses. Example: He passed the exam because he studied hard.
6. Do I need a comma before a coordinating conjunction?
A comma is needed when joining two independent clauses:
✅ She was tired, but she continued working.
❌ She was tired but continued working. (No comma, as the second part is not an independent clause.)
7. Can a sentence have multiple coordinating conjunctions?
Yes! Example:
- He wanted to go out, but it was raining, so he stayed home.
8. What is an example of coordinating conjunctions sharing the subject?
He came early and slept off.
She studied well but failed the test.
9. Are all coordinating conjunctions always necessary?
No, sometimes a simple sentence can be written without them. However, they are useful in connecting thoughts smoothly.
10. Can I use “and” and “but” in the same sentence?
Yes, but be mindful of clarity. Example:
She was tired, but she worked hard and finished on time.
Free admission and English Courses. കാശ് കൊടുക്കാതെ അഡ്മിഷൻ. FREE ഇഗ്ലീഷ് കോഴ്സുകൾ. ഈ ഓഫർ നേടൂ. Contact us at +91 9886926773 പ്രോസസ്സിംഗ് ആയാസകരം.

New batch is open. Join today!

Ready to study abroad or master OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English?
📞 Call us now at +91 9886926773
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: mail@goltc.in
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
