| Interlocutor Role Play Card Patient Setting: Community Health Centre |
| You are a 35-year-old vegetarian who does not cook owing to a hectic lifestyle, and mainly relies on ready meals for convenience. You drink 4-5 cups of coffee a day. Lately, you’ve been feeling exhausted. Your doctor has explained that you have anaemia (the number of red blood cells in your blood is low). You’ve been asked to speak to a nurse for dietary suggestions. TASK Explain to the nurse that you are confused by the diagnosis and how it relates to your diet (you choose vegetarian ready meals because you believe they are healthy). Answer the nurse’s questions regarding your dietary routine (coffee for breakfast, frozen meals for lunch, coffee and cake for afternoon tea, rarely eat dinner). Be resistant to the nurse’s suggestions as you dislike tofu and green leafy vegetables, coffee helps you cope with the stress of work. Finally agree to the recommendations but be adamant that you cannot reduce your coffee consumption. |
| Candidate Role Play Card Nurse Setting: Community Health Centre |
| You are speaking with a 35-year-old who has recently been diagnosed with anaemia (haemoglobin is 8g/dl). Their doctor has referred him/her to your centre for further advice concerning their condition and necessary dietary adjustments. TASK Find out if the patient has any questions regarding the diagnosis. Explain that iron is only sourced from the diet and can be low in vegetarians without planning. Reassure the patient it is treatable with dietary modification. Find out further details about the patient’s dietary habits. Suggest ways in which the patient can increase his/her iron intake (e.g. beans, leafy green vegetables such as spinach/kale, tofu, iron-fortified cereals, reduce consumption of coffee — inhibits absorption of iron). Discuss the importance of food combining as a compromise (allow one hour between consuming iron-rich food and coffee to increase absorption; Vitamin C at the same time as iron-rich food). |
All posts by Jomon P John
JUNIOR SPORTS INJURIES OET Reading
We hope this information has been valuable to you. If so, please consider a monetary donation to Lifestyle Training Centre via UPI. Your support is greatly appreciated.

Would you like to undergo training for OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English with us? Kindly contact us now!
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: [email protected]
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
JUNIOR SPORTS INJURIES OET READING ANSWERS
Part A
1. c
2. B
3. D
4. c
5. B
6. A
7. D
8. SERIOUS HEAD INJURIES
9. Protective head gear
10. Volleyball
11. Knee injuries
12. Do not further damage
13. Custom fabricated mouth guards
14. Recreational activities
15. Re-injury
16. Protective wrist guard
17. Soccer
18. Medical clearance
19. An appropriate qualified person
20. The female athlete
Part B
1. A
2. A
3. B
4. A
5. B
6. C
Part C (01)
1. B
2. C
3. B
4. A
5. B
6. C
7. D
8. A
Part C (02)
1. C
2. A
3. B
4. D
5. A
6. D
7. A
8. C
JUNIOR SPORTS INJURIES OET READINGOET READINGOET SPEAKINGOET ROLE PLAYSOET LETTER WRITINGOET LISTENINGWe hope this information has been valuable to you. If so, please consider a monetary donation to Lifestyle Training Centre via UPI. Your support is greatly appreciated.

Would you like to undergo training for OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English with us? Kindly contact us now!
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: [email protected]
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
TUBERCULOSIS OET READING
We hope this information has been valuable to you. If so, please consider a monetary donation to Lifestyle Training Centre via UPI. Your support is greatly appreciated.

Would you like to undergo training for OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English with us? Kindly contact us now!
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: [email protected]
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
TUBERCULOSIS OET READING
TEXT A Background: In New York City, the incidence of tuberculosis has more than doubled during the past decade. We examined the incidence of tuberculosis and the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and the rate of death from all cause in a very high-risk group – indigent subject who abuse drugs, alcohol, or both. Methods: In 2009 we began to study prospectively a cohort of welfare applicants and recipients 18 to64 years of age who abused or alcohol. The incidence rate of tuberculosis, AIDS, and death for this group were ascertained through vital records and New York City’s tuberculosis and AIDS registries.
TEXT B: RESULTS. The cohort was followed for eight years. Of the 858 subjects;
• tuberculosis developed in 47 (5.5 percent),
• 84 (9.8 percent) were given a diagnosis of AIDS, and
• 183 (21.3 percent) died.
The rates of incidence per 100,000 person- years were
• 744 for tuberculosis, • 1323 for AIDS, and., • 2842 for death.
In this group of welfare clients,
• the rate of newly diagnosed tuberculosis was 14.8 times that of the age matched general population of New York City;
• the rate of AIDS-was 10.0 times as high; • the death rate was 5.2 times as high.
• no significant difference in the rate of new cases of tuberculosis between subjects with positive skin tests and those with negative skin tests at examination in 2009.
TEXT C. Deaths in the cohort: There were 183 deaths in the cohort during follow-up (21.3 percent) of the subjects, a rate of 2842 deaths per 100,000 person-years, 5.2 times that of the age-matched general population. Causes of death – Table 3
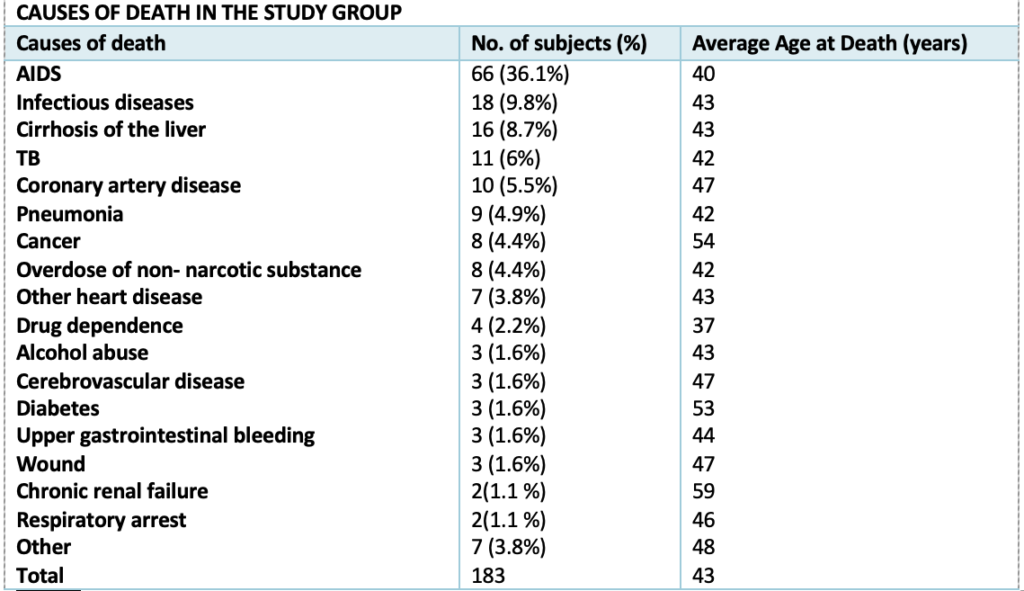
TEXT D: Conclusions
• Of the 47 subjects with tuberculosis, 21 (44.7 percent) died before the end of 2017;
• 12 (57.1 percent) of those who died also had AIDS.
• Of 15 persons with both tuberculosis and AIDS, 12 (80.0 percent) died before the end of 2017 and 8 died before completing anti-TB therapy.
• Of the 84 study subjects with AIDS, 68 (81.0 percent) died before the end of 2017.
For each question, 1-7, decide which text (A, B, C or D) the information comes from
1. what was the percentage of deaths caused by diabetes in the study group?
2. what was the rate of incidence per 100,000 person per years for tuberculosis?
3. name the city where the study was conducted?
4. how the incidence rates of diseases and death for the study group were ascertained?
5. how many died before the end of 2017 without completing anti-TB therapy?
6. what was the average age of subjects died due to other causes in the study group?
7. how many years the cohort was followed?
Questions 8-13. Answer each of the questions, 8-13, with a word or short phrase from one of the texts.
8. How many of the study subjects with only AIDS died before the end of 2017?
9. In how many of the study subjects wound was the cause of death?
10. What was the age limits of the study subjects?
11. When did the study begin?
12. What was the total number of deaths in the study group?
13. What was the percentage of deaths caused by respiratory arrest in the study group?
Questions 14-20. Complete each of the sentences, 14-20, with a word or short phrase.
14. The study shows that number of the incidence of tuberculosis in New York City has more than _____________during the past decade.
15. In conclusion, 12 of those who died had both AIDS and ____________
16. In the cohort during follow-up of the subjects, rate of deaths was 5.2 times that of the _______________ general population.
17. In the group of welfare clients, the rate of ________________ was 10.0 times as high.
18. The study was conducted among _____________ who abuse drugs, alcohol, or both.
19. ___________ subjects died suffering from coronary artery disease.
20. There were ______________ subjects in the study group.
PART B
Incubators for Infant: The general principle is that air is processed before it reaches baby. An electric fan draws room air through a bacterial filter which removes dust and bacteria. The filtered air flows over an electric heating element. The filtered and heated air then passes over a water tank where it is moistened. It then flows on to the incubator canopy. The incubator canopy is slightly pressurized. This allows expired carbon dioxide to pass back into the room via the vent holes and most of the air to be re-circulated. It also prevents unfiltered air entering the system.
1. The extract informs us that the incubators
A. is likely to circulate most of the air again.
B. may not work correctly in close proximity to some other devices.
C. prevents filtered air entering the system.
Nebulizers: A nebulizer is a device used to administer medication in the farm of a mist inhaled into the lungs. Nebulizers are commonly used for treatment of cystic fibrosis, asthma and other respiratory diseases. The reason for using a nebulizer for medicine to be administered directly to the lungs is that small aerosol droplets can penetrate into the narrow branches of the lower airways. Large droplets would be absorbed by the mouth cavity, where the clinical effect would be low. The common technical principle for all nebulizers is to use oxygen, compressed air or ultrasonic power as means to break up medical solutions or suspensions into small aerosol droplets.
2. The notice is giving information about
A: ways of checking that a nebulizer has been placed correctly1<
B. how the use of nebulizer is authorised.
C. why nebulizer is being used.
Oxygen Concentrators: Atmospheric air consists of approximately 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen. An oxygen concentrator uses air as a source of oxygen by separating these two components. It utilizes the property of zeolite granules to selectively absorb nitrogen from compressed air. Atmospheric air is gathered, filtered and raised to a pressure of 20 pounds per square inch (psi) by a compressor. The compressed air is then introduced into one of the canisters containing zeolite granules where nitrogen is selectively absorbed leaving the residual oxygen available for patient use. After about 20 seconds the supply of compressed air is automatically diverted to the second canister where the process is repeated enabling the output of oxygen to continue uninterrupted.
3. What does this manual tell us about zeolite granules?
A. leave residual oxygen for patient use
B. selectively absorb nitrogen from air
C. absorb only nitrogen from compressed air
Arterial blood pressure: The arterial blood pressure (BP) is connected with the force-, which is exerted by the blood volume on the walls of the arteries. The level of BP is dependent on two factors: the heart minute ejection volume and the elasticity of arterial walls. Other factors affecting BP include: the volume’ and viscosity of the blood, body position and emotional state. The BP at the top of pulse wave (due to the constriction of heart ventricles) is called systolic BP, whereas the respective one during the diastole is called diastolic BP. The difference between systolic and diastolic BP is defined as amplitude or pulse pressure.
4. Which is the main factor behind BP level?
A. the heart minute rejection volume
B. volume and viscosity of the blood
C. elasticity of the arterial wall
Basic Life Support: Basic Life Support means saving lives by maintaining airway, supplying ventilation (rescue breathing by blowing air to the victim’s mouth) and supplying circulation (external cardiac massage – chest compressions) performed without additional equipment. It is the first step in cardio pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) that should be initiated by bystanders and continued until qualified help arrives. Next step is Advanced Life Support (ALS), which is performed by medical services. People with cardiac arrest (CA) need immediate CPR. First aid means BLS that is started by witnesses before the emergency service arrival and is the key action in achieving patient survival.
5. What does this manual tell us about cardio-pulmonary resuscitatio?
A. should be initiated by bystanders
B. should be initiated immediately only for cardiac arrest
C. should be performed by medical services
Types of surgical threads: Materials, which the threads are made of, are divided into absorbable and non- absorbable ones or natural and synthetic sutures. Non-absorbable sutures are applied on the skin and in septic wounds. Absorbable threads, depending on their structure are divided into monofilament, polifilament, braided, plaits, coated and uncoated ones. Time of their absorbing is varied and depends on material properties; it can take from 14 days to 6 months. Absorbing progresses due to enzymatic disintegration and hydrolysis.
6. What does this extract from a handbook tell us about absorbable threads?
A. absorbing progresses due to enzymatic integration and hydrolysis7
B. absorbing time is varied and depends on material properties
C. are divided into monofilament, polifilament, braided; plaits and uncoated ones
PART C TEXT 1.
Targeting two important risk factors for cardiovascular disease and other major risk factors that can be lowered by modification, treatment or control
Paragraph 1: (ARA) – It’s well known that the prevalence of diabetes is on the rise. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 23.6 million, or nearly 8 percent of people in the United States, have diabetes, and 1.6 million new cases are diagnosed each year in people aged 20 and older. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for about 90 to 95 percent of those diagnosed, and occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not respond to insulin.
Paragraph 2: But something that many people may not know is that in addition to having diabetes, 70 percent of adult with type 2 diabetes also have high LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), the “bad” cholesterol that can cause build-up in the arteries, greatly increasing their risk for cardiovascular disease. Cholesterol is needed for the body to function normally, but when there is too much LDL-C in the bloodstream, it is deposited in arteries, including those of the heart, which can limit blood flow and lead to heart disease.
Paragraph 3: The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC) emphasize that it is critical to control both cholesterol and blood sugar levels. The ADA recommends that patients with type 2 diabetes aim for an A1C level which reflects your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months, of less than 7 percent. The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) ATP 111 recommends that patients with type 2 diabetes target an LDL-C goal of less than 100 mg/dL.
Paragraph 4: Treating these two diseases can take a combination of efforts, including a healthy diet and increased exercise. Medications are also sometimes needed. While there are many drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat type 2 diabetes and others available to lower LDL-C, a drug called Welchol (colesevelam HCI) is the first and only medication approved as an adjunct to diet and exercise to reduce both A1C in adults with type 2 diabetes and LDL-C in adults with elevated cholesterol.t
Welchol addresses both of these chronic health conditions with one medication and offers the convenience of two formulations, Welchol tablets and Welchol for Oral Suspension. Welchol can be taken alone or with other cholesterol lowering medications known as statins and can be added to other anti-diabetic medications (metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin).
Paragraph 5: “For patients with type 2 diabetes and high LDL cholesterol, it is important to manage both conditions,” said Yehuda Handelsman, MD, FACP, FACE, Medical Director of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif. “Welchol reduces these two risk factors for cardiovascular disease in adults with type 2 diabetes by significantly lowering A1C and LDL-C or ‘bad’ cholesterol, providing a unique therapeutic option.” It is important to note that the affect of Welchol on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
Paragraph 6: What are the major uncontrollable risk factors for coronary heart disease? The American Heart Association has identified several risk factors for coronary heart disease. Some of them can be modified, treated or controlled, and some can’t. The more risk factors a person has, the greater the chance that he or she will develop heart disease. Also, the greater the level of each risk factor, the greater the risk. For example, a person with a total cholesterol of 300 mg/dL has a greater risk than someone with a total cholesterol of 240 mg/dL, even though all people with a total cholesterol of 240 or higher are considered high risk.
Paragraph 7: Increasing age – About 82% of people who die of coronary heart disease are 65 or older.
Male sex (gender) – The lifetime risk of developing CHD after age 40 is 49% for men and 32% for women. The incidence of CHD in women lags behind men I years for total CHD and by 20 years for more serious clinical events such as sudden death.
Paragraph 8: Heredity (including Race)- Children of parents with heart disease are more likely to develop it themselves. African Americans have more severe high blood pressure than Caucasians and a higher risk of heart disease. Heart· disease is also higher among Mexican Americans, American Indians, native Hawaiians and some Asian Americans. This is partly due to higher rates of obesity and diabetes. Most people with a strong family history of heart disease have one or more other risk factors. Just as you can’t control your age, sex and race, you can’t control your family history. Therefore, it’s even more important to treat and control any other risk factors you have.
Paragraph 9: Other major risk factors that can be lowered by modification, treatment or control. Tobacco smoke – Smokers’ risk of developing CHD is two to four times that nonsmokers. Smokers who have a heart attack are more likely to die and die suddenly (within an hour) than nonsmokers. Cigarette smoking also acts with other risk factors to greatly increase the risk for coronary heart disease. People who smoke cigars or pipes seem to have a higher risk of death from coronary heart disease (and possibly stroke), but their risk isn’t as great as cigarette smokers’. Constant exposure to other people’s smoke – called environmental tobacco smoke, secondhand smoke or passive smoking – increases the risk of heart disease even for nonsmokers.
Paragraph 10: High blood cholesterol levels – The risk of coronary heart disease rises as blood cholesterol levels increase. When other risk factors (such as high blood pressure and tobacco smoke) are present, this risk increases even more. A person’s cholesterol level is also affected by age, sex, heredity and diet.
High blood pressure – High blood pressure increases the heart’s workload, causing the heart to enlarge and weaken over time. It also increases the risk of stroke, heart attack, kidney failure and heart failure. When high blood pressure exists with obesity, smoking, high blood cholesterol levels or diabetes, the risk of heart attack or stroke increases several times.
Paragraph 11: Physical inactivity-An inactive lifestyle is a risk factor for coronary heart disease. Regular, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity is important in preventing heart and blood vessel disease.
Obesity and overweight – People who have excess body fat – especially if a lot of it is in the waist area – are more likely to develop heart disease and stroke even if they have no other risk factors. Excess weight increases the strain on the heart, raises blood pressure and blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and lowers HDL (good) cholesterol levels. It can also make diabetes more likely to develop. Many obese and overweight people have difficulty losing weight. If you can lose as little as 10 to 20 pounds, you can help lower your heart disease risk.
Paragraph 12: Diabetes mellitus – Diabetes seriously increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Even when glucose levels are under control, diabetes greatly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. From two-thirds to three-quarters people with diabetes die of some form of heart or blood vessel disease.
Paragraph 13: What other factors contribute to heart disease risk? Stress – Individual response to stress may be a contributing factor. Some scientists have noted a relationship between coronary heart disease risk and stress in a person’s life, their health behaviors and socioeconomic status. These factors may affect established risk factors. For example, people under stress may overeat, start smoking or smoke more than they otherwise would.
Paragraph 14: Excessive alcohol intake – Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure, cause heart failure and lead to stroke. It can contribute to high triglycerides, cancer and other diseases, and produce irregular heartbeats. It also contributes to obesity, alcoholism, suicide and accidents. The risk of heart disease in people who drink moderate amounts of alcohol (an average of one drink for women or two drinks for men per day) is lower than in nondrinkers. One drink is defined as 1-1/2 fluid ounces (fl oz) of 80-proof spirits (such as bourbon, Scotch, vodka, gin, etc.), 1 fl oz of 100- proof spirits, 4 fl oz of wine, or 12 fl oz of beer. It’s not recommended that nondrinkers start using alcohol or that drinkers increase their intake.
Q1. According to paragraph 1 of the article states that
a. Diabetes has stabilised
b. 1.6 million people aged 20 and older have diabetes
c. Type 2 diabetes is the most common
d. Type 2 diabetes occurs when there is an over-production of insulin
Q2. In addition to having diabetes
a. 30% of adult with Type 2 diabetes do not have high counts of low-density lipids
b. 70% of adults with Type 2 diabetes do have high counts of low-density lipids
c. Too many LDLs in the bloodstream go straight to the heart
d. LDLs in the bloodstream cannot hinder blood flow
Q3. According to the ADA and the ACC
a. Both blood sugar levels and cholesterol levels need to be controlled if diabetes is avoided
b. Blood sugar levels need to be controlled if diabetes is to be avoided
c. ACA believes less than7% average blood sugar level over a one-month period indicates diabetes risk
d. The NCEP does not recommend Type 2 diabetics aim for less than 100 mg/dL of low-density lipids
Q4. Welchol, a drug to lower the level of LDLs in the blood
a. has not been approved by the U.S. FDA
b. Welchol must be taken with other statins
c. Welchol should not be added to medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas or insulin.
d. Welchol needs to be taken together with a healthy diet and an exercise program to reduce A1C in Type 2 diabetics and LDL-C in adults with elevated cholesterol levels.
Q5. Welchol’s effect on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality…
a. is supported by the evidence b. has not been positively established
c. has been positively established d. none of the above
Q6. Some risk factors can be controlled, or lowered; some cannot be controlled: such as advancing age, one’s gender, and one’s genetic inheritance. However, there are some major risk factors that can be lowered by modifying one’s lifestyle – or by medical intervention. Risk factors such as—–
a. high blood pressure b. high cholesterol levels c. obesity d. all of the above
Q7. The article states that stress
a. causes overeating and/or habitual smoking
b. does not interact with lifestyle and socioeconomic status
c. depends on how one reacts to it
d. may depend on how one reacts to it
Q8. Alcohol contributes to heart failure and strokes;
a. if you drink very less amount
b. moderate alcohol intake leads to less risk of heart disease
c. but not contribute to high triglycerides
d. is not a factor in developing cancer
PART C. TEXT 2. FLUORIDE
Paragraph 1: Globalization has provoked changes in many facets of human life, particularly in diet. Trends in the development of dental caries in population have traditionally followed developmental patterns where, as economies grow and populations have access to a wider variety of food products as a result of more income and trade, the rate of tooth decay begins to increase. As countries become wealthier, there is a trend to greater preference for a more “western” diet, high m carbohydrates and refined sugars. Rapid globalization of many economies has accelerated this process. These dietaries have a substantial impact on diseases such as diabetes and dental caries.
Paragraph 2: The cariogenic potential of diet emerges in areas where fluoride supplementation is inadequate. Dental caries is a global health problem and has a significant negative impact on quality of life, economic productivity, adult and children’s general health and development. Untreated dental caries in pre-school children is associated with poorer quality of life, pain and discomfort, and difficulties in ingesting food that can result in failure to gain weight and impaired cognitive development. Since low-income countries cannot afford dental restorative treatment and in general the poor are most vulnerable to the impacts of illness, they should be afforded a greater degree of protection.
Paragraph 3: By WHO estimates, one third of the world’s population have inadequate access to needed medicines primarily because they cannot afford them. Despite the inclusion of sodium fluoride in the World Health Organization’s Essential Medicines Model List, the global availability and accessibility of fluoride for the prevention of dental caries remains a global problem. The optimal use of fluoride is an essential and basic public health strategy in the prevention and control of dental caries, the most common non communicable disease on the planet. Although a whole range of effective fluoride vehicles are available for fluoride use (drinking water, salt, milk, varnish, etc.), the most widely used method for maintaining a constant low level of fluoride in the oral environment is fluoride toothpaste.
Paragraph 4: More recently, the decline in dental caries amongst school children in Nepal has been attributed to improved access to affordable fluoride toothpaste. For many low-income nations, fluoride toothpaste is probably the only realistic population strategy for the control and prevention of dental caries since cheaper alternatives such as water or salt fluoridation are not feasible due to poor infrastructure and limited financial and technological resources. The use of topical fluoride e.g., in the form of varnish or gels for dental caries prevention is similarly impractical since it relies on repeated applications of fluoride by trained personnel on an individual basis and therefore in terms of cost cannot be considered as part of a population based preventive strategy.
Paragraph 5: The use of fluoride toothpaste is largely dependent upon its socio-cultural integration in personal oral hygiene habits, availability and the ability of individuals to purchase and use it on a regular basis. The price of fluoride toothpaste is believed to be too high in some developing countries and this might impede equitable access. In a survey conducted at a hospital dental clinic in Lagos, Nigeria 32.5% of the respondents reported that the cost of toothpaste influenced their choice of brands and 54% also reported that the taste of toothpastes influenced their choice.
Paragraph 6: Taxes and tariffs on fluoride toothpaste can also significantly contribute to high prices, lower demand and inequity since they target the poor. Toothpastes are u; classified as a’ cosmetic product and as such often highly taxed by governments. For example, various taxes such as excise tax, VAT, local taxes as well as taxation on the ingredients and packaging contribute to 25% of the retail cost of toothpaste in Ne and India, and 50% of the retail price in Burkina Faso. WHO continues to recommend the removal taxes and tariffs on fluoride toothpastes. Any lost revenue can be rest by higher taxes on sugar and high sugar containing foods, which are common risk factors for dental caries, coronary heart disease, diabetes and obesity.
Paragraph 7: The production of toothpaste within a country has the potential to make fluoride toothpaste more affordable than imported products. In Nepal, fluoride toothpaste was limited to expensive imported products. However, due to successful advocacy locally manufactured fluoride toothpaste, the least expensive locally manufactured fluoride toothpaste is now 170 times less costly than the most expensive imported Philippines, local manufacturers are able to satisfy consumer preferences and compete against multinationals by discounting the price of toothpaste by as much as 55% against global brands; and typically receive a 40% profit margin compared to 70% for multinational producers.
Paragraph 8: In view of the current extremely inequitable use of fluoride throughout countries and regions, all efforts to make fluoride and fluoride toothpaste affordable and accessible must be intensified. As a first step to addressing the issue of affordability of fluoride toothpaste in the poorer countries in-depth country studies should be undertaken to analyze the price of toothpaste in the context of the country economies.
Q1. Which of the following would be the most appropriate heading for the paragraph 1?
a. High sugar intake and increasing tooth decay
b. Globalisation, dietary changes and declining dental health
c. Dietary changes in developing nations
d. Negative health effects of a western diet
Q2. Which of the following is not mentioned as a negative effect of untreated dental caries in pre-school children?
a. Decreased mental alertness b. Troubling chewing and swallowing food
c. Lower life quality d. Reduced physical development
Q3. According to paragraph 3, which of the following statement is correct?
a. Dental caries is the most contagious disease on earth.
b. Fluoride in drinking water is effective but rarely used
c. Fluoride is too expensive for a large proportion of the global population.
d. Fluoride toothpaste is widely used by 2/3 of the world’s population.
Q4. Fluoride toothpaste is considered the most effective strategy to reduce dental caries in low-income countries because___
a. it is the most affordable.
b. topical fluoride is unavailable.
c. it does not require expensive infrastructure or training.
d. it was effective in Nepal.
Q5. Which of the following is closest in meaning to the word impede?
a. stop b. prevent c. hinder d. postpone
Q6. Regarding the issue of taxation in paragraph 6 which of the following statements is most correct?
a. Income tax rates are higher in Burkina Faso than India or Nepal.
b. WHO recommends that tax on toothpaste be reduced.
c. Governments would like to reduce tax on toothpastes but can’t as it is classified as a cosmetic.
d. WHO suggests taxing products with a high sugar content instead of toothpastes.
Q7. Which of the following is closest in meaning to the _word advocacy?
a. marketing b. demand c. development d. support
Q8. Statistics in paragraph 7 indicate that….
a. local products can’t compete with global products and make a profit at the same time.”
b. Philippine produced toothpaste is profitable while being less than half the price of global brands.
c. in Nepal, fluoride toothpaste is limited to imported products which are very expensive
d. toothpaste produced in the Philippines has a higher profit margin than internationally produced toothpaste.
We hope this information has been valuable to you. If so, please consider a monetary donation to Lifestyle Training Centre via UPI. Your support is greatly appreciated.

Would you like to undergo training for OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English with us? Kindly contact us now!
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: [email protected]
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
Would you like to download a copy of the practice test? Please click on the download button below:

TUBERCULOSIS OET READING ANSWERS
Text A
01. C
02. B
03. A
04. A
05. D
06. C
07. B
08. 58
09. 3
10. 18 TO 64 years
11.2009
1.2. 183
13.1,.1%
14. Doubieci
15. Tuberculosis
16. Age – matched
17. AIDS
18. lndigent subject
19. 10
20.858
Text B
01. A
02. C
03. C
04. C
05. A
06. B
Text c(Part 01)
01. C
02. B
03. A
04. D
05. B
06. D
07. D
08. B
Text c (Part 02)
01. B
02. A
03. C
04. C
05. C
06. D
07. D
08. B
TUBERCULOSIS OET READINGOET READINGOET SPEAKINGOET ROLE PLAYSOET LETTER WRITINGOET LISTENINGWe hope this information has been valuable to you. If so, please consider a monetary donation to Lifestyle Training Centre via UPI. Your support is greatly appreciated.

Would you like to undergo training for OET, PTE, IELTS, Duolingo, Phonetics, or Spoken English with us? Kindly contact us now!
📱 Call/WhatsApp/Text: +91 9886926773
📧 Email: [email protected]
Visit us in person by following the directions on Google Maps. We look forward to welcoming you to the Lifestyle Training Centre.
Follow Lifestyle Training Centre on social media:
Thank you very much!
Conjunctive adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs are words that function as both adverbs and connectors, linking independent clauses or sentences. They help express relationships such as cause and effect, contrast, comparison, or sequence. Common conjunctive adverbs include therefore, however, moreover, nevertheless, consequently, furthermore, and meanwhile.
Accordingly – used to show a result or consequence Example: He failed the test; accordingly, he has to retake the class.
Also – used to add information or to show a relationship between two ideas Example: She is an excellent pianist; also, she can sing very well.
Besides – used to add information or to show a relationship between two ideas Example: The store has a great selection of clothes; besides, their prices are very reasonable.
Consequently – used to show a result or consequence Example: She missed the train; consequently, she was late for work.
Hence – used to show a result or consequence Example: The car broke down; hence, we had to call a tow truck.
However – used to show a contrast or comparison Example: She loves swimming; however, she is afraid of deep water.
Indeed – used to emphasize a point or to show agreement Example: He is a great athlete; indeed, he is the best in the team.
Meanwhile – used to show a contrast or comparison between two actions happening at the same time Example: She is studying for her exams; meanwhile, her brother is watching TV.
Moreover – used to add information or to show a relationship between two ideas Example: He is very smart; moreover, he has a great sense of humor.
Nevertheless – used to show a contrast or comparison Example: The movie was boring; nevertheless, she watched it until the end.
Similarly – used to show a comparison between two ideas or things Example: He plays the guitar; similarly, his sister plays the piano.
Therefore – used to show a result or consequence Example: He was late for work; therefore, he missed an important meeting.
Thus – used to show a result or consequence Example: The project was successful; thus, we received an award for it.
By using conjunctive adverbs, writers can create more complex and varied sentences, which can make their writing more interesting and effective.
CONTRAST CONJUNCTIONS
Contrast conjunctions are words or phrases used to express opposition or difference between ideas or elements in a sentence. They help highlight distinctions, contradictions, or conflicting relationships. Common contrast conjunctions include but, yet, however, although, even though, nevertheless, on the other hand, and in contrast.
Examples:
But: used to show a contrast or an exception. Example: She is smart, but she is not very organized.
Yet: used to show a contrast or a contradiction. Example: He works hard, yet he does not get good grades.
However: used to show a contrast or a limitation. Example: She is very talented; however, she lacks experience.
Although: used to show a contrast or a concession. Example: Although it was raining, they went to the beach.
While: used to show a contrast or a comparison. Example: She is quiet, while her sister is very talkative.
Whereas: used to show a contrast or a comparison. Example: He likes spicy food, whereas she prefers mild food.
Despite: used to show a contrast or a contradiction. Example: Despite the bad weather, they went camping.
In contrast: used to show a comparison or a difference. Example: She is very outgoing; in contrast, her sister is shy.
On the other hand: used to show a contrast or an alternative. Example: He likes to stay up late; on the other hand, his sister goes to bed early.
Instead: used to show a contrast or a substitution. Example: She decided to stay home instead of going to the party.
By using contrast conjunctions, writers can create a more complex and nuanced text, showing the differences between ideas, events, and characters in their writing.
CORRELATIVE CONJUNCTIONS:
Examples:
(1) Both…and: used to show that two things are true or that two things should be considered together. Example: Both my sister and my brother enjoy playing the piano.
(2 )Either…or: used to show a choice between two things. Example: You can either go to the beach or go to the park.
(3) Neither…nor: used to indicate that both options are negative. Example: Neither the teacher nor the students were happy with the test results.
(3) Not only…but also: used to add emphasis to two related ideas or to show that two things are true. Example: Not only did she win the competition, but she also broke the record.
(4) Whether…or: used to show a choice between two options or alternatives. Example: I am not sure whether to take the job or wait for a better opportunity.
(5) As…as: used to show an equal comparison between two things. Example: She is as intelligent as she is beautiful.
(6) Such…that: used to indicate a result or consequence. Example: The rain was so heavy that we had to cancel the picnic.
(7) No sooner…than: used to show that one thing happened immediately after another. Example: No sooner had she finished her homework than she started watching TV.
Subordinating conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions link two parts of a sentence, making it more complex. They connect a dependent clause (incomplete thought) to an independent clause (complete thought). These words, like after, because, and when, show relationships like time, cause-and-effect, or contrast between the clauses.
Examples:
- After: ശേഷം
It is used to indicate that one event will occur following another event.
Example: After I finish my work, I will go for a walk.
I will go for a walk after I finish my work. (no comma) - Although/ Though/ Eventhough: എങ്കിലും, ആയിരുന്നാലും, എന്നിട്ടും, ആണെങ്കിലും
It is used to express a contrast or contradiction.
Example: Although it was raining, we decided to go for a picnic.
We decided to go for a picnic, although it was raining. (need comma in both formation) - As: ആ സമയത്ത് , ആയതിനാൽ
It is used to indicate that two actions are happening simultaneously.
Example: As I was walking to the store, I saw a friend.
As I was not well, I din’t go to school.
I didn’t go to school as I was sick (no need for comma) - Because: അതുകൊണ്ട്
It is used to indicate the reason for something.
Example: I couldn’t attend the party because I was feeling sick.
Because I was feeling sick, I couldn’t attend the party. (need comma) - Before: മുമ്പ്
It used to indicate that one event will occur prior to another event.
Example: Before you judge others, (you) judge yourself. (need comma)
Judge yourself before you judge others (no need of comma) - Even if: എന്നാലും
It is used to express a hypothetical or unlikely situation.
Example: Even if it rains tomorrow, we will still go to the beach.
We will still go to the beach even if it rains tomorrow. - If: എങ്കിൽ
It is used to express a hypothetical or conditional situation.
Example: If I study hard, I can pass the exam. (need comma)
I can pass the exam if I study hard. (no need of comma) - In order that: അതിനായി
It is used to express purpose or intent.
Example: I will study hard in order that I can get a good grade on the test.
In order that I can get a good grade on the test, I will study hard. - In order to: ഇതിനായി
In order to get good sleep, one should go to bed early.
One should go to bed early in order to get good sleep. - Once: ഒരു കാര്യം പൂർത്തിയാക്കിയ ശേഷം
It is used to indicate that an event will occur after another event has taken place.
Example: Once you reach home, please call me.
Please call me once you reach home. - Provided that ഒരു വ്യവസ്ഥ നിറവേറ്റിയാൽ
It is used to express a condition that must be met in order for something to happen
Example:I will give you a promotion provided that you achieve your target.
Provided that you achieve your target, I will give you a promotion. - Since ആയതിനാൽ, അതുകൊണ്ട്
Example: Since it’s raining outside, we decided to have a cozy movie night indoors. - So that: അതുകൊണ്ട്
It is used to express purpose or intent.
Example: I will study hard so that I can get a good grade on the test.
So that I can get a good grade on the test, I will study hard. - Unless അല്ലാതെ
it is used to express a condition that must be met in order for something to happen.
Example: I won’t be able to attend the meeting unless I finish my work on time. - Until അതുവരെ
It is used to indicate that an event will continue until another event occurs. (time)
Example: I will keep working until I finish the project. - When ആ സമയത്ത്
It is used to indicate that an event will occur at the same time as another event.
Example: When you reach, please call me.
Please call me when you reach. - Whereas: അതേസമയം
It is used to express a contrast or comparison
Example: She likes action movies, whereas I prefer romantic comedies. - Wherever: എവിടെയായിരുന്നാലും
It is used to indicate any place where something may happen.
Example: I will follow you wherever you go.
Wherever you go, I will follow you. - While: അതെ സമയം
It is a conjunction that is commonly used to indicate a contrast, opposition, or simultaneous occurrence of two actions. Its meaning can vary depending on the context in which it’s used. Here are a few common uses of “while” as a conjunction:
A. Contrast:
She enjoys reading while her brother prefers playing video games.
While some people prefer summer, others prefer winter.
B. Simultaneous Action:
I listened to music while I worked on my assignment.
He ate dinner while watching TV.
C. Time:
I met her while I was studying abroad.
While I was in the store, I ran into an old friend.
More examples of subordinating conjunctions
1. After:
– After the rain stopped, we went outside to play.
– We went outside to play after the rain stopped.
– After I finish my chores, I’ll join you for dinner.
– I’ll join you for dinner after I finish my chores.
2. Although:
– Although it was late, she decided to go for a run.
– She decided to go for a run, although it was late.
– Although he studied hard, he still failed the exam.
– He still failed the exam, although he studied hard.
3. As:
– As I was walking to the store, I saw an old friend.
– I saw an old friend as I was walking to the store.
– She smiled at me as if she knew something I didn’t.
– As if she knew something I didn’t, she smiled at me.
4. As if:
– He acted as if he had never seen a dog before.
– He had never seen a dog before, as if he acted.
– She looked at me as if I had grown another head.
– As if I had grown another head, she looked at me.
5. As long as:
– You can stay up late as long as you finish your homework.
– As long as you finish your homework, you can stay up late.
– As long as the food is delicious, I’ll eat anything.
– I’ll eat anything as long as the food is delicious.
6. As much as:
– As much as I love ice cream, I know it’s not good for me.
– I know it’s not good for me, as much as I love ice cream.
– As much as he wanted to go on vacation, he couldn’t afford it.
– He couldn’t afford it, as much as he wanted to go on vacation.
7. As soon as:
– As soon as the bell rings, you can leave the classroom.
– You can leave the classroom as soon as the bell rings.
– She knew the answer as soon as the question was asked.
– As soon as the question was asked, she knew the answer.
8. As though:
– He acted as though he had seen a ghost.
– He had seen a ghost, as though he acted.
– She talked to me as though I were a child.
– As though I were a child, she talked to me.
9. Because:
– They cancelled the picnic because of the bad weather.
– Because of the bad weather, they cancelled the picnic.
– She didn’t go to the party because she wasn’t feeling well.
– Because she wasn’t feeling well, she didn’t go to the party.
10. Before:
– Before she goes to bed, she reads a book.
– She reads a book before she goes to bed.
– He likes to have his coffee before he starts work.
– Before he starts work, he likes to have his coffee.
11. By the time:
– By the time she arrived, the party was already over.
– The party was already over by the time she arrived.
– By the time we finish the project, the deadline will have passed.
– The deadline will have passed by the time we finish the project.
12. Even if:
– Even if it rains, we’ll still go to the beach.
– We’ll still go to the beach, even if it rains.
– Even if he apologizes, I’m not sure I can forgive him.
– I’m not sure I can forgive him, even if he apologizes.
13. Even though:
– Even though it was his birthday, he didn’t want to celebrate.
– He didn’t want to celebrate, even though it was his birthday.
– Even though she studied hard, she failed the exam.
– She failed the exam, even though she studied hard.
14. If:
– If it rains, we’ll stay indoors.
– We’ll stay indoors if it rains.
– If he arrives late, we’ll start without him.
– We’ll start without him if he arrives late.
15. Inasmuch as:
– Inasmuch as I appreciate the offer, I have to decline.
– I have to decline inasmuch as I appreciate the offer.
– Inasmuch as he wants to help, he doesn’t know how.
– He doesn’t know how, inasmuch as he wants to help.
16. In case:
– Take an umbrella in case it rains.
– In case it rains, take an umbrella.
– I brought some snacks in case we get hungry.
– In case we get hungry, I brought some snacks.
17. In order that:
– I’ll leave early in order that I can catch the train.
– In order that I can catch the train, I’ll leave early.
– She turned up the volume in order that she could hear better.
– In order that she could hear better, she turned up the volume.
18. Lest:
– Turn off the lights lest they attract mosquitoes.
– Lest they attract mosquitoes, turn off the lights.
– She wrote a reminder lest she forget about the meeting.
– Lest she forget about the meeting, she wrote a reminder.
19. Now that:
– Now that we’re here, let’s enjoy ourselves.
– Let’s enjoy ourselves, now that we’re here.
– Now that he has a job, he can afford to buy a car.
– He can afford to buy a car, now that he has a job.
20. Once:
– Once you finish your homework, you can go out and play.
– You can go out and play once you finish your homework.
– Once the sun sets, it will be too dark to play outside.
– It will be too dark to play outside once the sun sets.
21. Provided (that):
– You can go to the party provided that you finish your homework first.
– Provided that you finish your homework first, you can go to the party.
– We can go for a walk provided that it stops raining.
– Provided that it stops raining, we can go for a walk.
22. Rather than:
– He chose to walk rather than take the bus.
– Rather than take the bus, he chose to walk.
– She decided to apologize rather than argue further.
– Rather than argue further, she decided to apologize.
23. Since:
– Since it’s already late, let’s go to bed.
– Let’s go to bed since it’s already late.
– Since he already knows the answer, there’s no need to ask him.
– There’s no need to ask him since he already knows the answer.
24. So that:
– He opened the window so that fresh air could come in.
– So that fresh air could come in, he opened the window.
– She left a note on the table so that we wouldn’t forget.
– So that we wouldn’t forget, she left a note on the table.
25. Supposing (that):
– Supposing that you don’t pass the test, what will you do?
– What will you do, supposing that you don’t pass the test?
– Supposing that it rains, we should bring umbrellas.
– We should bring umbrellas, supposing that it rains.
26. Than:
– She is taller than her sister.
– Her sister is shorter than she is.
– He would rather walk than take the bus.
– Than take the bus, he would rather walk.
27. That:
– He said that he would come to the party.
– I know that you can do better than this.
– She believes that honesty is the best policy.
– It’s possible that she forgot about the meeting.
28. Though:
– Though it was raining, they decided to go for a walk.
– They decided to go for a walk, though it was raining.
– He failed the exam, though he studied hard.
– Though he studied hard, he failed the exam.
29. Till:
– We’ll wait here till you arrive.
– Till you arrive, we’ll wait here.
– He worked till late in the night to finish the project.
– Till late in the night, he worked to finish the project.
30. Unless:
– Unless you apologize, I won’t forgive you.
– I won’t forgive you unless you apologize.
– We won’t be able to go out unless the rain stops.
– Unless the rain stops, we won’t be able to go out.
31. Until:
– We’ll wait here until you finish your presentation.
– Until you finish your presentation, we’ll wait here.
– She stayed up until midnight studying for her exam.
– Until midnight, she stayed up studying for her exam.
32. When:
– I’ll call you when I reach the airport.
– When I reach the airport, I’ll call you.
– He always gets nervous when he has to speak in public.
– When he has to speak in public, he always gets nervous.
33. Whenever:
– Whenever she hears that song, it reminds her of her childhood.
– It reminds her of her childhood whenever she hears that song.
– He always brings flowers whenever he visits his grandmother.
– Whenever he visits his grandmother, he always brings flowers.
34. Where:
– This is where we first met.
– We first met where you’re standing.
– She looked everywhere to find her keys, but she couldn’t remember where she left them.
– She couldn’t remember where she left them, even though she looked everywhere to find her keys.
35. Whereas:
– She enjoys sweet foods, whereas her sister prefers savory dishes.
– Whereas her sister prefers savory dishes, she enjoys sweet foods.
– He enjoys spending time outdoors, whereas his brother prefers staying indoors.
– Whereas his brother prefers staying indoors, he enjoys spending time outdoors.
36. Wherever:
– She’ll follow her dreams wherever they may lead.
– Wherever they may lead, she’ll follow her dreams.
– He always carries his camera wherever he goes.
– Wherever he goes, he always carries his camera.
37. Whether:
– Whether you like it or not, we have to finish this project by tomorrow.
– We have to finish this project by tomorrow, whether you like it or not.
– She couldn’t decide whether to go to the party or stay home.
– Whether to go to the party or stay home, she couldn’t decide.
38. While:
– I like to listen to music while I’m working.
– While I’m working, I like to listen to music.
– She called her friend while she was waiting for the bus.
– While she was waiting for the bus, she called her friend.
39. Because of:
– She couldn’t attend the meeting because of a family emergency.
– Because of a family emergency, she couldn’t attend the meeting.
– He was late to the party because of heavy traffic.
– Because of heavy traffic, he was late to the party.
40. In spite of:
– In spite of the rain, they decided to go for a picnic.
– They decided to go for a picnic in spite of the rain.
– In spite of his busy schedule, he always finds time for his hobbies.
– He always finds time for his hobbies in spite of his busy schedule.
41. Despite:
– Despite the bad weather, they went ahead with the outdoor party.
– They went ahead with the outdoor party despite the bad weather.
– Despite his busy schedule, he always finds time for his family.
– He always finds time for his family despite his busy schedule.
42. Even when:
– Even when it’s late, he insists on finishing his work.
– He insists on finishing his work even when it’s late.
– Even when she was tired, she kept practicing the piano.
– She kept practicing the piano even when she was tired.
43. Whether or not:
– Whether or not she agrees, we’re going ahead with the plan.
– We’re going ahead with the plan whether or not she agrees.
– Whether or not it rains, the picnic will still take place.
– The picnic will still take place whether or not it rains.
44. No matter:
– No matter what happens, I’ll always be there for you.
– I’ll always be there for you, no matter what happens.
– No matter how hard she tries, she can’t seem to please everyone.
– She can’t seem to please everyone, no matter how hard she tries.
45. So long as:
– You can use my car so long as you fill up the tank afterward.
– So long as you fill up the tank afterward, you can use my car.
– He’s allowed to play video games so long as he finishes his homework first.
– So long as he finishes his homework first, he’s allowed to play video games.
46. In the event that:
– In the event that the power goes out, we have flashlights and candles.
– We have flashlights and candles in the event that the power goes out.
– He packed an extra jacket in the event that it gets cold.
– In the event that it gets cold, he packed an extra jacket.
47. Insofar as:
– Insofar as I know, the meeting is still scheduled for tomorrow.
– The meeting is still scheduled for tomorrow, insofar as I know.
– She followed the instructions insofar as she understood them.
– Insofar as she understood them, she followed the instructions.
48. Provided (that):
– You can borrow my car provided that you return it by Friday.
– Provided that you return it by Friday, you can borrow my car.
– We’ll go to the beach provided that the weather stays nice.
– Provided that the weather stays nice, we’ll go to the beach.
49. Whether or not:
– Whether or not he apologizes, I won’t forgive him.
– I won’t forgive him whether or not he apologizes.
– Whether or not they win the game, they’ll still celebrate.
– They’ll still celebrate whether or not they win the game.
50. Seeing that:
– Seeing that you’re tired, let’s call it a day and continue tomorrow.
– Let’s call it a day and continue tomorrow, seeing that you’re tired.
– Seeing that she’s upset, he decided to postpone the conversation.
– He decided to postpone the conversation, seeing that she’s upset.